Embedded Participant (also known as Scenario Guide, Scenario Role Player, or Confederate)
a role assigned in a simulation encounter to help guide the scenario. The guidance may be influential as positive, negative, or neutral or as a distracter, depending on the objective(s), the level of the participants, and the scenario. Although the embedded participant’s role is part of the situation, the underlying purpose of the role may not be revealed to the participants in the scenario or simulation.
Debriefing
An activity that follows a simulation experience and is led by a facilitator. Participants’ reflective thinking is encouraged, and feedback is provided regarding the participants’ performance while various aspects of the completed simulation are discussed. Participants are encouraged to explore emotions and question, reflect, and provide feedback to one another. The purpose of debriefing is to move toward assimilation and accommodation to transfer learning to future situations
Critical Thinking
A disciplined process that requires validation of data, including any assumptions that may influence thoughts and actions, and then careful reflection on the entire process while evaluating the effectiveness of what has been determined as the necessary action(s) to take. This process entails purposeful, goal-directed thinking and is based on scientific principles and methods (evidence) rather than assumptions or conjecture.
Evaluation
- A broad term for appraising data or placing a value on data gathered through one or more measurements. It involves rendering a judgment including strengths and weaknesses. Evaluation measures quality and productivity against a standard of performance.
Facilitator
An individual who provides guidance, support, and structure during simulation-based learning experiences.
Feedback
Information given or dialogue between participants, facilitator, simulator, or peer with the intention of improving the understanding of concepts or aspects of performance.
High Fidelity
Experiences using full scale computerized patient simulators, virtual reality or embedded participants that are extremely realistic and provide a high level of interactivity and realism for the learner.
Inter-professional
When students from two or more professions learn about, from and with each other to enable effective collaboration and improve health outcomes.
Low Fidelity
Experiences such as case studies, role-playing, using partial task trainers, or static mannequins to immerse students or professionals in a clinical situation or practice of a specific skill.
Moulage
Techniques used to simulate injury, disease, aging, and other physical characteristics specific to a scenario. Moulage supports the sensory perceptions of participants and supports the fidelity of the simulation scenario through the use of makeup, attachable artifacts, and smells.
Objective
The statement(s) of specific measurable results that participant (s) is expected to achieve during a simulation-based experience.
Pre-briefing (Briefing)
An information or orientation session held prior to the start of a simulation- based learning experience in which instructions or preparatory information is given to the participants. The purpose of the pre-briefing or briefing is to set the stage for a scenario and assist participants in achieving scenario objectives. Suggested activities in a pre-briefing or briefing include an orientation to the equipment, environment, mannequin, roles, time allotment, objectives, and patient situation.
Safe Learning Environment
The emotional climate that facilitators create by the interaction between facilitators and participants. In this positive emotional climate, participants feel at ease taking risks, making mistakes, or extending themselves beyond their comfort zone. Facilitators should be thoroughly aware of the psychological aspects of learning, aware of the effects of unintentional bias, aware of cultural differences, and attentive to their own state of mind in order to effectively create a safe environment for learning.
Scenario or Clinical Scenario
The plan of an expected and potential course of events for a simulated clinical experience. The clinical scenario provides the context for the simulation and can vary in length and complexity, depending on the objectives. The clinical scenario design includes:
- Participant preparation
- Pre-briefing (Briefing): review of objectives, instructions prior to implementation of scenario, questions, or other resources used in the scenario.
- Patient information describing the situation to be managed.
- Participant objectives.
This model, developed by the International Nursing Association for Clinical Simulation and Learning,
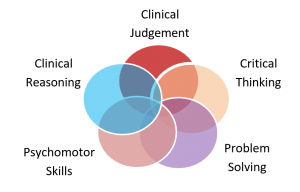 reflects the complexity of skill development necessary to progress from more basic skills to the higher-level clinical judgment and reasoning ability used in decision making for safe, effective nursing practice. All levels of development are interrelated, therefore, they interact and affect one another.
reflects the complexity of skill development necessary to progress from more basic skills to the higher-level clinical judgment and reasoning ability used in decision making for safe, effective nursing practice. All levels of development are interrelated, therefore, they interact and affect one another.- Environmental conditions, including manikin, setting, or embedded participant preparation.
- Related equipment, props, and tools or resources for assessing and managing the simulated experience to increase the realism.
- Roles, expectations, or limitations of each role to be played by participants.
- A progression outline including a beginning and an ending.
- Debriefing and Evaluation criteria
Simulated-Based Learning Experience
An array of structured activities that represent actual or potential simulations in education and practice and allow participants to develop or enhance knowledge, skills and attitudes or analyze and respond to realistic situations in a simulated environment or through an unfolding case study.
Standardized Patient
A person trained to consistently portray a patient or other individual in a scripted scenario for the purposes of instruction, practice, or evaluation.
1 Meakim, C., Boese, T., Decker, S., Franklin, A. E., Gloe, D., Lioce, L., Sando, C. R., & Borum, J. C. (2013, June). Standards of Best Practice: Simulation Standard I: Terminology. Clinical Simulation in Nursing, 9(6S), S3-S11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2013.04.001. 2013 International Nursing Association for Clinical Simulation and Learning. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
